updated 2020-06
Contents:
1. Fantic History
2. Fantic, Broncco, Concord and Gary Models
3. Concord Parts
1. Fantic History
Garelli was an major Italian motorcycle and moped manufacturer , founded in 1919 by engineer Adalbarto Garelli.
Agrati was an Italian scooter manufacturer, founded in 1958. Agrati produced the 70cc, 80cc and 125cc Capri, the Rex Monaco and the 48cc Como. In 1960 Agrati merged with Garelli and used the name Agrati Garelli until about 1978.

 Fantic Motor was founded in 1968 by Dr. Mario Agrati of Agrati Garelli, and Henry Keppel-Hesselink, who was responsible for foreign sales at Agrati Garelli. Fantic first produced a line of mini-bikes, go-karts and mini-enduro bikes, branded as Broncco for the American youth market.
Fantic Motor was founded in 1968 by Dr. Mario Agrati of Agrati Garelli, and Henry Keppel-Hesselink, who was responsible for foreign sales at Agrati Garelli. Fantic first produced a line of mini-bikes, go-karts and mini-enduro bikes, branded as Broncco for the American youth market.
From cybermotorcycle.com
In 1969 the Lombard factory at Sede e Stabilimento: via Statale, 22061 Barzago (CO) launched the famous 50cc Caballero which immediately met success with younger riders due to its technical superiority and competitive pricing. In 1973 the first 125 appeared, powered by a Minarelli engine built specifically for Fantic.
Late 1970’s and early 80’s Fantic mopeds also had Minarelli engines built specifically for Fantic. See Minarelli engine scroll down to V1 engine fan versions and head versions. The Minarelli C2 also had Fantic coverings. Fantic engines were mostly made by Minarelli but always said “Fantic Motor”.
 Broncco minibikes and enduro bikes were made by Fantic and sold by Engine Specialties, in Cornwells Heights, Pennsylvania. The 1969 to 1970 TC-4, TS-4 and BC-4 models were made by Agrati Garelli and had Garelli engines. All other Broncco models were made by Fantic Motor. The 1968 Broncco logo is the same as Fantic, suggesting it’s hidden identity.
Broncco minibikes and enduro bikes were made by Fantic and sold by Engine Specialties, in Cornwells Heights, Pennsylvania. The 1969 to 1970 TC-4, TS-4 and BC-4 models were made by Agrati Garelli and had Garelli engines. All other Broncco models were made by Fantic Motor. The 1968 Broncco logo is the same as Fantic, suggesting it’s hidden identity.
So Agrati, Garelli, Fantic and Broncco were connected in the late 1960’s and 70’s. Sources are Wheels of Italy, Wikipedia-Garelli, and Fantic Motor Heritage.

Concord is a brand of US model Fantic mopeds, 1978 to 1980. The US importer/distributor was Wheelsport, 2424 NE Riverside Way, Portland Oregon. Both Fantic and Concord brands were sold in the US from about 1976 to 1981.
Fantic was successful in enduro competition and won the world championship in 1981. After 1981 their logo said “world champion”.
 Fabbrica Motoveicoli: European motorcycle makers were struggling in the late 1980’s. Many were forced into bankruptcy followed by government ownership and control. Fabbrica Motoveicoli S.p.a. began managing Fantic from April 1987.
Fabbrica Motoveicoli: European motorcycle makers were struggling in the late 1980’s. Many were forced into bankruptcy followed by government ownership and control. Fabbrica Motoveicoli S.p.a. began managing Fantic from April 1987.
Gary: Around 1990 Fabbrica Motoveicoli also acquired the Agrati Garelli brand.
The 1990’s moped was a modernized 1984-86 Garelli Basic, called Gary.
Gary models had Garelli horizontal one speed pedal, and 1 or 2 speed kick start engines. 
See Garelli Models.
The Fantic Motor factory closed in 1995. Under new ownership production resumed in 2005.
2. Fantic, Broncco, Concord and Gary Models
from Sheldons EMU and official sales flyers or ads
UK models from Funky Mopeds by Richard Skelton
colors: off road, mini, off-road mini, moped, noped

1968 Fantic from oldminibikes.com

’68 Broncco TC-4 Cross
US 0cc hp 0 tires 1968 xxxxx xxxxxxxxxx engine
EU 172 3.8 3.50 – 7 Fantic TX-1 x-xxxxxxxx Aspera OHV
EU 172 2.8 3.50 – 7 Fantic TX-2 x-xxxxxxxx Aspera OHV
EU 172 2.8 3.50 – 7 Fantic TX-3 x-xxxxxxxx Aspera OHV
EU 172 2.8 3.00 – 5 Fantic TX-4 x-xxxxxxxx Aspera OHV
EU 172 2.8 3.50 – 5 Fantic Fun Kart xxxxxx Aspera OHV
US 172 3.8 3.50 – 7 Fantic Broncco T/X-1 x Aspera OHV
US 172 2.8 3.50 – 7 Fantic Broncco T/X-2 x Aspera OHV
US 172 2.8 3.50 – 7 Fantic Broncco T/X-3 x Aspera OHV
US 172 2.8 3.00 – 5 Fantic Broncco T/X-4 x Aspera OHV
US 172 2.8 3.50 – 5 Fantic Broncco Fun Kart Aspera OHV
US 050 5.0 3.00-10 Garelli Broncco T/C-4 Cross Garelli 354 4M

1969 Fantic

1969 Broncco

1969 Broncco TC-4 engine
US 0cc hp 0 F tire o0 R tire 1969 xxxxx xxxxxxxxx engine
EU 172 3.8 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Fantic TX-1 xxxxxxxxx Aspera OHV
EU 172 2.8 3.00 - 5 3.00 - 5 Fantic TX-3 xxxxxxxx Aspera OHV
EU 050 0.0 2.50-19 3.00-17 Fantic TX-9 Caballero Minarelli P4SS
US 172 3.8 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Fantic Broncco T/X-1D Aspera OHV
US 172 2.8 3.00 - 5 3.00 - 5 Fantic Broncco T/X-3 Aspera OHV
US 172 2.8 3.50 - 5 3.50 - 5 Fantic Broncco Fun Kart Aspera OHV
US 050 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Garelli Broncco T/C-4 Garelli 354 4M

1970 Broncco from oldminibikes.com

’70 Broncco Karts

1970 Fantic Fantichino

1970 Broncco TX-6

1970 Broncco TX-7 restored by Bill Small

’70 Broncco TS-4

1970 Broncco TS-4 with Garelli 354 engine

1970 Broncco BC-4

1970 Broncco TC-4
US 0cc hp 0 F tire o0 R tire 1970 xxxxx xxxxxxxxx engine
EU 060 1.0 2.50 - 5 2.50 - 5 Fantic Fantichino xxxx Fantichino
EU 050 5.0 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Fantic TX-6 xxxxxxxx Minarelli P4S
EU 050 1.5 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Fantic TX-7 Mini-matic Minarelli V1
EU 050 1.5 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Fantic TX-7 Mini-matic Minarelli V1K
EU 050 6.0 2.50-19 3.00-17 Fantic TX-9 Caballero Minarelli P4SS
US 172 3.0 3.00 - 5 3.00 - 5 Fantic Broncco TX-4 x Aspera OHV
US 050 5.0 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Fantic Broncco TX-6 x Minarelli P4S
US 050 1.5 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 F Broncco TX-7 (pedal) Min. V1 CEV6831
US 050 1.5 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Fantic Broncco TX-7 x Min. V1K CEV6831
US 172 3.0 3.50 - 5 3.50 - 5 Broncco Fun Kart xxx Aspera OHV
US 172 3.0 3.50 - 5 3.50 - 5 Broncco Dune Kart xx Aspera OHV
US 050 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Garelli Broncco BC-4 Garelli G4mk
US 050 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Garelli Broncco TS-4 Garelli 354-4M
US 050 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Garelli Broncco TC-4 Garelli 354-4M

’71 Broncco Apache 100

1971 Broncco Diablo

1971 Broncco from oldminibikes.com
US 0cc hp 0 F tire o0 R tire 1971 xxxxx xxxxxxxxx engine
US 060 1.0 2.50 - 5 2.50 - 5 Broncco Fantichino xxxx Fantichino
US 172 3.0 3.00 - 5 3.00 - 5 Broncco Colt (TX-4) xxx Aspera OHV
US 172 3.0 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Broncco Tomahawk xxxx Aspera OHV
US 172 3.0 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Broncco Marauder xxxxx Aspera OHV
US 172 4.0 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Broncco Trailblazer xxxx Aspera OHV
US 050 1.5 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Broncco Deputy (TX-7) x Minarelli V1
US 050 1.5 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Broncco Deputy (TX-7) x Minarelli V1K
US 050 5.0 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Broncco Wrangler (TX-6) Minarelli P4S
US 070 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Broncco Diablo (TX-10) Min. P470 auto
US 070 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Broncco Diablo (TX-10) xMinarelli P470
EU 050 1.5 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Fantic TX7 Mini-matic xx Minarelli V1
EU 050 1.5 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Fantic TX7 Mini-matic xx Minarelli V1K
EU 050 5.0 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Fantic TX6 xxx xx xx xx Minarelli P4S
EU 070 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Fantic TX10 xx xx xx xx Min. P470 auto
EU 070 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Fantic TX10 xx xx xx xx Minarelli P470
EU 050 6.0 2.50-19 3.00-17 Fantic TX9 Caballero xx Minarelli P4SS
EU 100 12 2.50-19 3.00-17 Fantic Caballero 100 xx Minarelli 100/5
US 100 12 2.50-19 3.00-17 Broncco Apache 100 xx Minarelli 100/5
US 172 3.0 3.50 - 5 3.50 - 5 Broncco Fun Kart xxxxx Aspera OHV
US 172 3.0 3.50 - 5 3.50 - 5 Broncco Dune Kart xxx Aspera OHV
===== 13 of 14 Broncco models listed =====
Fantic in UK: (from Wikipedia) Fantic began exporting to the United Kingdom in 1972, as part of a wave of manufacturers who took advantage of “sixteener laws,” legislation that forbade sixteen-year-old motorcyclists from riding motorcycles up to 250 cc, as they had been used to. As a result, European and Japananese manufacturers exported their sporty and lightweight below-50cc engines, which had been common in Europe, to England also. Fantic produced a “sensational chopper moped” and a TI “Turismo Internazionale”, both of which became very popular quickly, with the reputation of being some of the fastest mopeds on the market.

1972 Broncco

1972 TI and TX7

1972 Broncco
US 0cc hp 0 F tire o0 R tire 1972 xxxxx xxxxxxxxx engine
US 172 2.8 3.50 - 7 3.50 - 7 Broncco Renegade xx Aspera OHV
US 050 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Broncco Warrior xxxx Minarelli P4S
US 070 8.5 3.00-12 4.00-10 Broncco Eagle xxxxxx Minarelli P470
US 070 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Broncco Diablo xxxxx Minarelli P470
US 070 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Broncco Ranger xxxx Min. P470 auto
EU 050 1.5 3.00-10 3.00-10 Fantic TX7 Mini-matic Minarelli V1
EU 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6
UK 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6P
EU 050 6.8 2.75-16 5.00-16 Fantic Chopper xxxxx Minarelli P6E
UK 050 6.8 2.75-16 5.00-16 Fantic Chopper xxxxx Minarelli P6EP
EU 070 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Fantic Ranger xxxxxx Min. P470 auto
EU 070 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Fantic Diablo xxxxxx Minarelli P470
EU 050 1.5 3.00-12 4.00-10 Fantic Super Rocket x Minarelli P4A
EU 050 7.2 2.50-19 3.00-17 Fantic Caballero 4M x Minarelli P4E
EU 050 7.2 2.50-19 3.00-17 Fantic Caballero 6M x Minarelli P6E
EU 100 12 2.50-19 3.00-17 Fantic Caballero 100 Minarelli
Barron: (from Wikipedia) The Fantic Motor motorcycles were first imported into the U.K. in 1972 by Barron Eurotrade Ltd whose headquarters were based at 51 High Street Hornchurch, Essex… The Fantic T.I. quickly became a worthy contender with the rapid growth of a dealer network. The six speed gearbox was a strong selling point, and the perky Italian Minarelli 49cc P6 engine (6-speed with pedals) proved to be very reliable. Stories of the T.I. model reaching 70 mph were an exaggeration, as only just over 50-55 mph could be achieved, and in the right conditions.




1. ’73 Diablo, 2. ’73 Ranger, 3. ’73 Chopper, 4. ’73 Chopper
US 0cc hp 0 F tire o0 R tire 1973 xxxxx xxxx xxxxx engine
EU 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6
UK 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6P
EU 050 6.8 2.75-16 5.00-16 Fantic Chopper xxxxx Minarelli P6E
UK 050 6.8 2.75-16 5.00-16 Fantic Chopper xxxxx Minarelli P6EP
EU 070 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Fantic Ranger xxxxxx Min. P470 auto
EU 070 5.0 3.00-10 3.00-10 Fantic Diablo xxxxxx Minarelli P470
EU 050 1.5 3.00-12 4.00-10 Super Rocket xxxxxx Minarelli P4A
EU 050 6.8 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 4M xxxxxx Minarelli P4E
EU 050 6.8 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 6M xxxxxx Minarelli P6E
EU 125 0.0 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 125 xxxxxx Minarelli
EU 125 0.0 2.75-16 5.00-16 Chopper 125 xxxxxx Minarelli


1. ’74 Fantic, 2. ’74 Super Rocket
R means Regolarità (regulated)
RC means Regolarità Competizion (competition regulated)
US 0cc hp 0 F tire o0 R tire 1974xxxxx xxxxxxxxx engine
EU 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6
UK 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6P
UK 050 6.8 2.75-16 5.00-16 Fantic Chopper xxxx Minarelli P6EP
EU 050 1.5 3.00-12 4.00-10 Fantic Super Rocket Minarelli P4A
EU 050 1.5 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 50 SS xxxx Minarelli
EU 050 6.8 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 50 R 4M x Minarelli P4E
EU 050 7.2 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 50 R 6M x Minarelli P6E
UK 050 7.2 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 50 RC 6M Minarelli P6EP
EU 125 0.0 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 125 RC xx Minarelli 125/5
EU 125 0.0 2.75-16 5.00-16 Fantic Chopper 125 Minarelli 125/5

’75 Caballero 50 R Casa
US 0cc hp 0 F tire o0 R tire 1975 xxxxx xxxx xxxx engine
EU 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6
UK 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6P
EU 050 6.8 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic GT Super 6 x Minarelli P6E
EU 050 1.5 3.00-12 4.00-10 Fantic Super Rocket Minarelli P4A
EU 050 1.5 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 50 R Casa Minarelli P4A
EU 050 7.2 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 50 RC 6M Minarelli P6E
UK 050 7.2 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 50 RC 6M Minarelli P6EP
EU 125 0.0 2.50-19 3.00-17 Caballero 125 RC 5M Minarelli 125/5
EU 125 0.0 2.75-16 5.00-16 Chopper 125 xxxxxx Minarelli 125/5

1976 Fantic Lei (US)
US 0cc hp 0 F tire o0 R tire 1976 xxxxx xxxx xxxx engine
EU 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6
UK 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6P
US 050 1.5 3.00-10 3.00-10 Fantic Lei xxxx xxxxx Minarelli V1
EU 050 6.8 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic GT Super 6 xx Minarelli P6E
EU 050 1.5 3.00-12 4.00-10 Fantic Super Rocket x Minarelli P4A
EU 050 1.5 2.50-21 3.50-18 Caballero 50 R Casa x Minarelli P4A
EU 125 0.0 2.50-21 3.50-18 Caballero 125 RC 5M Minarelli 125/5
EU 125 0.0 2.50-21 3.50-18 Caballero 125 RC 6M Minarelli 125/6



1. 1977 Fantic GT Super 6 pedal (UK)
2. 1977 Fantic Lei, partial restoration by B. Small
3. 1977 Fantic Lei, from Caroline Smolen
US 0cc hp 0 F tire o0 R tire 1977 xxxxx xxxx xxxxx engine
EU 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6
UK 050 6.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic TI Turismo Int. Minarelli P6P
US 050 1.5 3.00-10 3.00-10 Fantic Lei
EU 050 1.5 2.25-16 2.25-16 Fantic Issimo
EU 050 1.5 3.00-10 3.00-10 Fantic Lei
EU 050 9.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic GT Super 6, 9hp 65mph
UK 050 9.0 2.75-17 2.75-17 Fantic GT Super 6, 9hp 65mph
EU 050 1.5 3.00-12 4.00-10 Fantic Super Rocket Minarelli P4A
EU 050 1.5 2.50-21 3.50-18 Caballero R Casa xx Minarelli P4A
EU 125 0.0 2.50-21 3.50-18 Caballero RC 6M xx Minarelli 125/6
EU 125 0.0 2.50-21 3.50-18 Trial 125
Concord is the brand name of US model Fantic mopeds. The US importer/distributor was Wheelsport, 2424 NE Riverside Way, Portland Oregon. Concord is not in any 1976-78 USA moped books and guides, so it appears they began in late 1978 or 1979.
In 1978 there was one model, Concord XKE, a mono-tube frame type moped with Minarelli V1 engine. In 1980 and perhaps late 1979 there were 3 more Concord models; Invader, Shadow and Freedom. In the 1980’s Los Angeles CA area there were only Concord moped dealers and no Fantic. In other states and all other countries there were only Fantic dealers and no Concord.

1978 Caballero 125

1978 Concord XKE (US)

Concord parts book
US 0cc hp 1978 xxxxx xxxx xxxx engine
US 050 1.5 Concord XKE xx xxxx Minarelli V1
US 050 1.5 Fantic Lei xxxxx xxxx Minarelli V1
EU 050 1.5 Fantic Issimo xxxxxx Minarelli V1
US 050 1.5 Fantic Issimo xxxxxx Minarelli V1
EU 050 1.5 Fantic Lei xxxxx xxxx Minarelli V1K
US 050 1.5 Fantic Pepi Sport xxx Minarelli V1
EU 050 9.0 Fantic GT Super 6 x Minarelli P6E
UK 050 9.0 Fantic GT Super 6 x Minarelli P6EP
EU 050 0.0 Super Rocket xxxxxx Minarelli P4A
EU 050 0.0 Caballero 50 R Casa Minarelli P4A
EU 125 0.0 Caballero 125 RC 6M Minarelli
EU 125 0.0 Fantic Trial 125 xxxx Minarelli

’79 Fantic Lei
TX-170

’79 Fantic Issimo

1979 Issimo
Confort

1979 Concord XKE
with Roger Staubach

Concord XKE features

1979 Issimo
Super Confort

1979 Issimo
Convert

1979 Issimo
Convert Super

1979 Fantic Lei

1979 Fantic
Super Rocket
US 0cc hp 1979 xxxxx xxxx xxxxx engine
US 050 1.5 Concord XKE xx xxxxx Minarelli V1
US 050 1.5 Fantic Lei xxxx xx xxx Minarelli V1
US 050 1.5 Fantic Issimo xxx xxx Minarelli V1
US 050 1.5 Fantic Pepi Sport xxxx Minarelli V1
EU 050 1.5 Fantic Issimo xxx xxx Minarelli V1
EU 050 1.5 Issimo Comfort xxxxx Minarelli V1K
EU 050 1.5 Issimo Super Comfort Minarelli V1K
EU 050 1.5 Issimo Convert xxxxx Minarelli C2
EU 050 1.5 Issimo Convert Super Minarelli C2
EU 050 1.5 Fantic Lei xxx xxx xxx Minarelli V1K
EU 050 9.0 Fantic GT Super 6 x Minarelli P6E
UK 050 9.0 Fantic GT Super 6 x Minarelli P6EP
EU 050 1.5 Super Rocket xxxxxx Minarelli P4A
EU 050 1.5 Caballero 50 R Casa Minarelli P4A
EU 050 7.2 Caballero 50 RC xx Minarelli P6E
EU 070 0.0 Caballero 70 RC xxx Minarelli
EU 125 0.0 Caballero 125 RC xx Minarelli
EU 125 0.0 Trial 125
EU 200 0.0 Trial 200
1980 Concords are in the Motorcyclist Magazine 1981 Moped and Economy Motorcycle Buyers Guide:
Concord Shadow is same as Fantic Pepi Sport, “5-star” mag wheels, top tank 1980-81 list $775
Concord Invader is same as Fantic Issimo Standard, spoke wheels, solo seat 1980-81 list $650?
Concord Freedom is almost Fantic Issimo Super Confort mags and long seat 1980-81 list $700

’80 Fantic Issimo (US)

’80 Concord Shadow

’80 Pepi Sport (US)

’80 Concord Invader

’80 Concord Freedom

’80 Fantic Issimo SC
US 0cc hp 1980 xxxxx xxxx xxxxx engine
US 050 1.5 Concord XKE xx xxxxx (Minarelli V1)
US 050 1.5 Fantic Lei xxxx xx xxx (Minarelli V1)
US 050 1.5 Fantic Issimo xxx xxx (Minarelli V1)
US 050 1.5 Fantic Pepi Sport xxx (Minarelli V1)
EU 050 1.5 Fantic Issimo xxx xxx (Minarelli V1)
EU 050 1.5 Issimo Comfort xxxxx (Minarelli V1K)
EU 050 1.5 Issimo Super Comfort (Minarelli V1K)
EU 050 1.5 Issimo Convert xxxxx (Minarelli C2)
EU 050 1.5 Issimo Convert Super (Minarelli C2)
EU 050 1.5 Fantic Lei xxx xxx xxx (Minarelli V1K)
EU 050 9.0 Fantic GT Super 6 x (Minarelli P6E)
UK 050 9.0 Fantic GT Super 6 x (Minarelli P6EP)
EU 050 0.0 Fantic Super Rocket
EU 050 1.5 Caballero 50 R Casa (Minarelli P4A)
EU 050 0.0 Caballero 50 RC
EU 070 0.0 Caballero 70 RC
EU 125 0.0 Caballero 125 RC
EU 125 0.0 Fantic Trial 125
EU 200 0.0 Fantic Trial 200
1981 was the first year of mandatory VIN label and manufacturer requirements for on-road motor vehicles worldwide. To avoid or delay having to do that, many European moped manufacturers produced extra inventory in 1980, that was stockpiled and later sold in 1981-84. That, and their focus on off-road, is probably why there are no 1981-83 on-road Fantic models.
1981
080 Enduro Competizione
125 Fantic Caballero 125 RC
200 Fantic Trial 200

1982 80 Comp.
From Sheldons EMU: In order to offer a product at the height of modern technology, the Barzago company established a racing department which contributed significantly to the development of Fantic with excellent results; they won the 1981 enduro world title. After 1981 their logo said “world champion”. The 1980’s saw Fantic offer a substantial model range that included road bikes and numerous specialty off-road machines. In competition trials more fine results accrued with rider Thierry Michaud winning three world titles for Fantic. Despite the quality of the product and impressive sports results, by the late 1980’s the Lombard company faced considerable economic difficulties. Japanese competition contributed to the collapse of many European motorcycle manufacturers in the 1980’s.
1982
080 Enduro Competizione
125 Fantic Caballero 125 RC
240 Fantic Trial 240
1983
125 Fantic Caballero 125 RC
240 Fantic Trial 240

’84 Fantic Sprinter
1984
050 Fantic Sprinter
125 Fantic Caballero 125 RC
240 Fantic Trial 240
1985
050 Fantic Sprinter
125 Fantic Caballero 125 RC
250 Fantic Raider 250
240 Fantic Trial 240

’86 Fantic Issimo
1986
050 Fantic Issimo
125 Fantic Caballero 125 RC
250 Fantic Raider 250

After 1985-86 European countries, starting with Germany, stopped requiring pedals on mopeds. Many other countries and some US states soon followed.
Fabbrica Motoveicoli: Fabbrica Motoveicoli S.p.a. began managing Fantic from April 1987.
1987-89 250 Fantic Raider
 Gary Around 1990 Fabbrica Motoveicoli also acquired the Agrati Garelli brand. The 1990’s moped was a modernized 1984-86 Garelli Basic, called Gary. It had Garelli horizontal one or two speed engines. See Garelli Models.
Gary Around 1990 Fabbrica Motoveicoli also acquired the Agrati Garelli brand. The 1990’s moped was a modernized 1984-86 Garelli Basic, called Gary. It had Garelli horizontal one or two speed engines. See Garelli Models.

1990 Gary Uno

1985 Garelli Basic
1990-93
050 Gary Uno
050 Gary Due
050 Gary Due Special
080 Fantic RC (cross)
250 Raider Fantic
1994-95 80 RC (cross)
From Sheldons EMU: In 1995 Fantic production ceased. The brand was auctioned and bought by industrialist Frederick Fregnan who gave new life to the famous Lombard marque, and from 2005 to 2017+ a variety of new models was on offer. Thierry Michaud became head of trials at FIM, and was such in 2017.
Today they continue in the same genre, though the names have changed to dual-sport and motard (supermoto), and they have not returned to the US market. Fantic launched in 2015 also new models of electric bikes, the Fat Bike.
2005 50cc Caballero Regolarità Casa,
2006 50cc Caballero Supersei (motard), Regolarità Competizione
2007 50cc Caballero Supersei (motard), 125cc Caballero air cooled (motard), Caballero Regolarità AC aircooled
2008 50cc Caballero Supersei (motard), Regolarità Competizone
0000 125cc Caballero AC (motard), Regolarità AC aircooled
2009 50cc Caballero Supersei (motard), 125cc Caballero water cooled (motard), Caballero AC (motard),
0000 Caballero Regolarità AC (enduro), 200cc Caballero Regolarità
2010 50cc Caballero Supersei (motard), 125cc Caballero water cooled (motard), Caballero AC (motard)
0000 Caballero Regolarità AC
2011-12 125cc Caballero water cooled (motard)
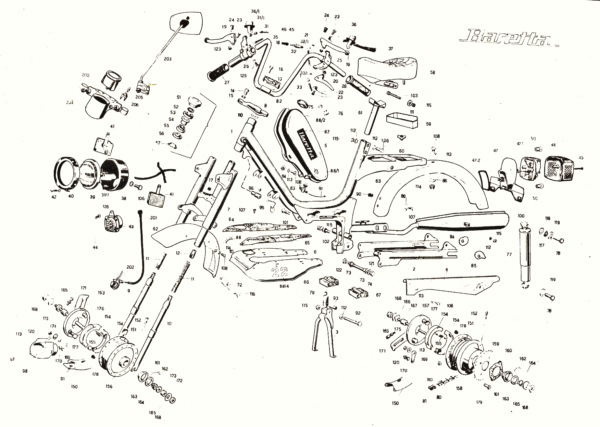
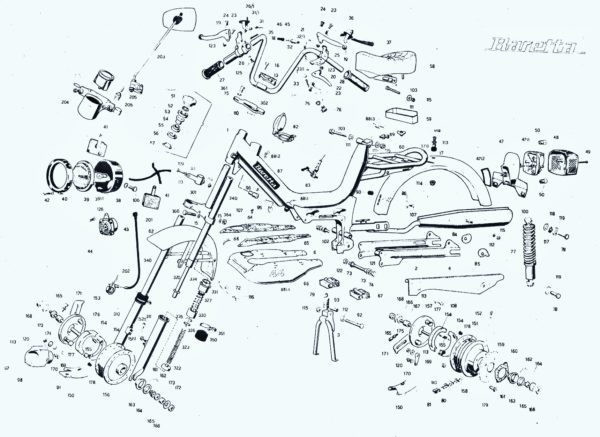
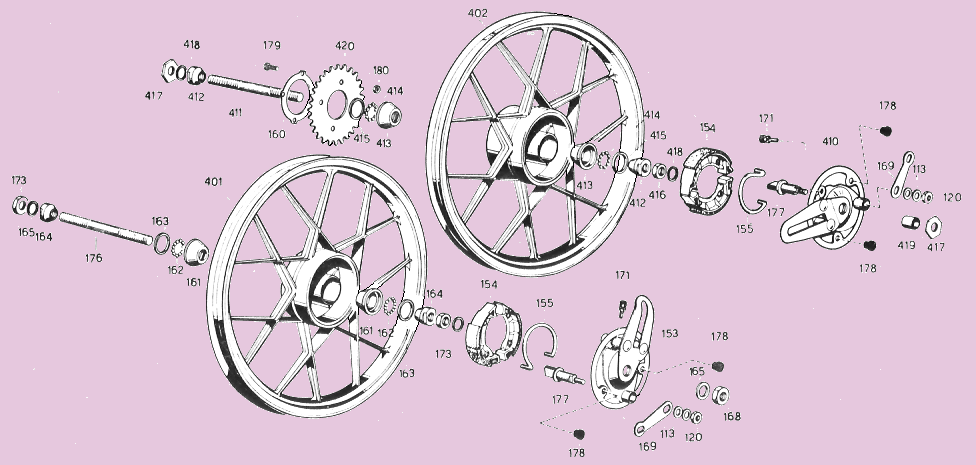
3. Concord Parts
Engine versions and Components:

Info 1980 Concord

Minarelli V1 versions
Concord 1978-79 XKE, Fantic Lei Minarelli V1 early (up to ’79)
grey fan cover, larger fan, small fins head, 38.8mm piston (25mph) or 38.0 (20mph)
Speed versions 25(1.5hp), 20(1.0hp), Dellorto SHA 14/12 (or 14/9 for 20mph) carburetor

Concord XKE gas cap threads 42 x 1.5

Concord XKE with Domino long controls

Concord XKE

1980 Concord XKE
and Roger Staubach
Concord 1979-80 Invader, Freedom, Shadow, Fantic Issimo Minarelli V1 “Fantic”
black Fantic fan cover, smaller fan, large Fantic square head. 38.7mm? piston
Speed version 25mph (1.5hp), Dellorto SHA 14/12 carburetor
CEV “pancake” head light, CEV “diamond” switches, Domino chrome controls and levers,
Grimeca aluminum mag wheels or spoke wheel hubs and 90mm brakes, CEV 6932 magneto,
Veglia speedometer with RH driver, and reflectors.
driver, and reflectors.

1980 Concord Freedom XKE 25
can be 10 male or 12 fem petcock

’80 C. Freedom
12×1 fem. down

1980 Concord Freedom
10×1 male spigot down

 The 1977-80 sheet frame Robin has a clockwise 3-wire Dansi 101813 magneto with an external ignition ground.
The 1977-80 sheet frame Robin has a clockwise 3-wire Dansi 101813 magneto with an external ignition ground. Moto Guzzi Robin (sheet frame) components: 2.25-16″ tires, Benelli one speed automatic engine, Dellorto SHA 14/9 carburetor, #45 jet. Dansi 101441 or 101813 magneto, see above. CEV 2143 headlight, CEV 9350 tail light, CEV round chrome clamp-on switches, PV controls, Grimeca hubs (rear hub is special, Benelli only) and brakes, no speedometer (has front basket instead), LH speedo driver, 12×1 female spigot left or back gas valve.
Moto Guzzi Robin (sheet frame) components: 2.25-16″ tires, Benelli one speed automatic engine, Dellorto SHA 14/9 carburetor, #45 jet. Dansi 101441 or 101813 magneto, see above. CEV 2143 headlight, CEV 9350 tail light, CEV round chrome clamp-on switches, PV controls, Grimeca hubs (rear hub is special, Benelli only) and brakes, no speedometer (has front basket instead), LH speedo driver, 12×1 female spigot left or back gas valve.
![]() Moto Guzzi (mono-tube frame) components: 2.25-16″ tires, Benelli one speed automatic engine, Dellorto SHA 14/9 carburetor, #44 jet. Dansi 101813 magneto (external ignition ground type). CEV 2139 bullet head light, CEV 9400.2 tail light (with resistor for external ignition ground magneto), CEV plastic slide clamp-on switches, PV controls, Grimeca hubs (rear hub is special, Benelli only) and brakes, Veglia speedometer with LH driver, 12×1 female gas valve with special long detachable shaft that goes through a hole in the side panel.
Moto Guzzi (mono-tube frame) components: 2.25-16″ tires, Benelli one speed automatic engine, Dellorto SHA 14/9 carburetor, #44 jet. Dansi 101813 magneto (external ignition ground type). CEV 2139 bullet head light, CEV 9400.2 tail light (with resistor for external ignition ground magneto), CEV plastic slide clamp-on switches, PV controls, Grimeca hubs (rear hub is special, Benelli only) and brakes, Veglia speedometer with LH driver, 12×1 female gas valve with special long detachable shaft that goes through a hole in the side panel.











































































 i
i